Computed attribute
This feature is available in version
2.7.2or later
Like many storage solutions, Casewhere supports computed attributes, for which, instead of accepting values set by applications, Casewhere will compute values from given expressions. Casewhere still persists computed attributes in the database, so features like indexing, searching still work as designed for these attributes.
Configuration
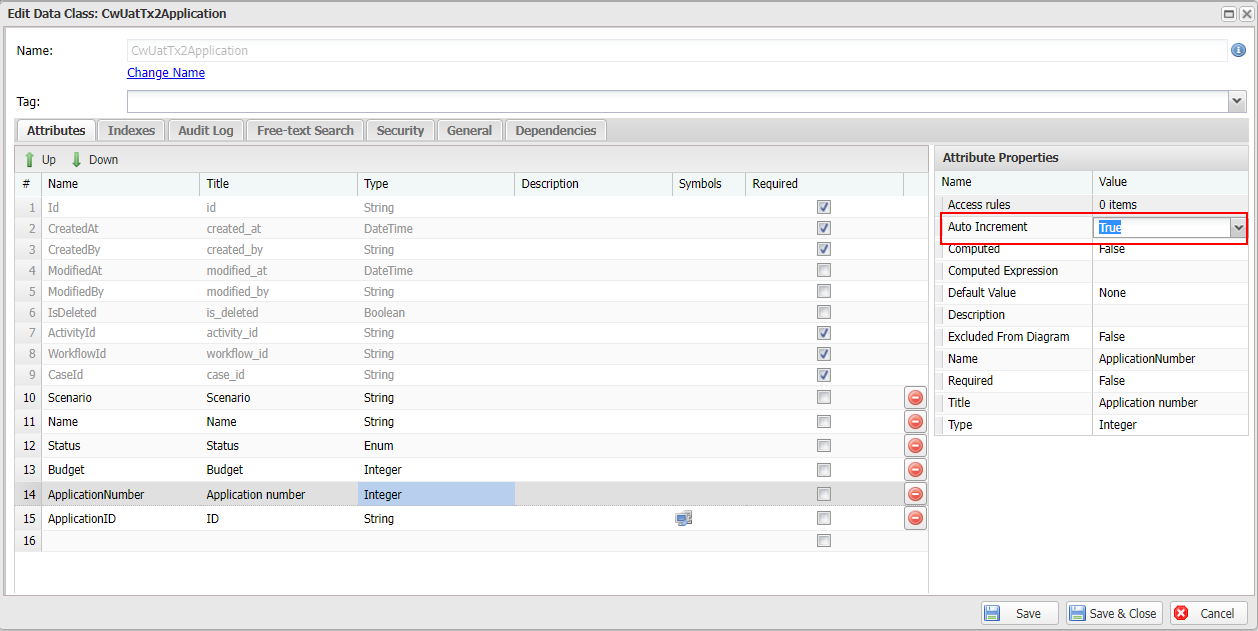
In the data class editor, select an attribute and set Computed to True. It's possible to enable Computed for any data attribute.
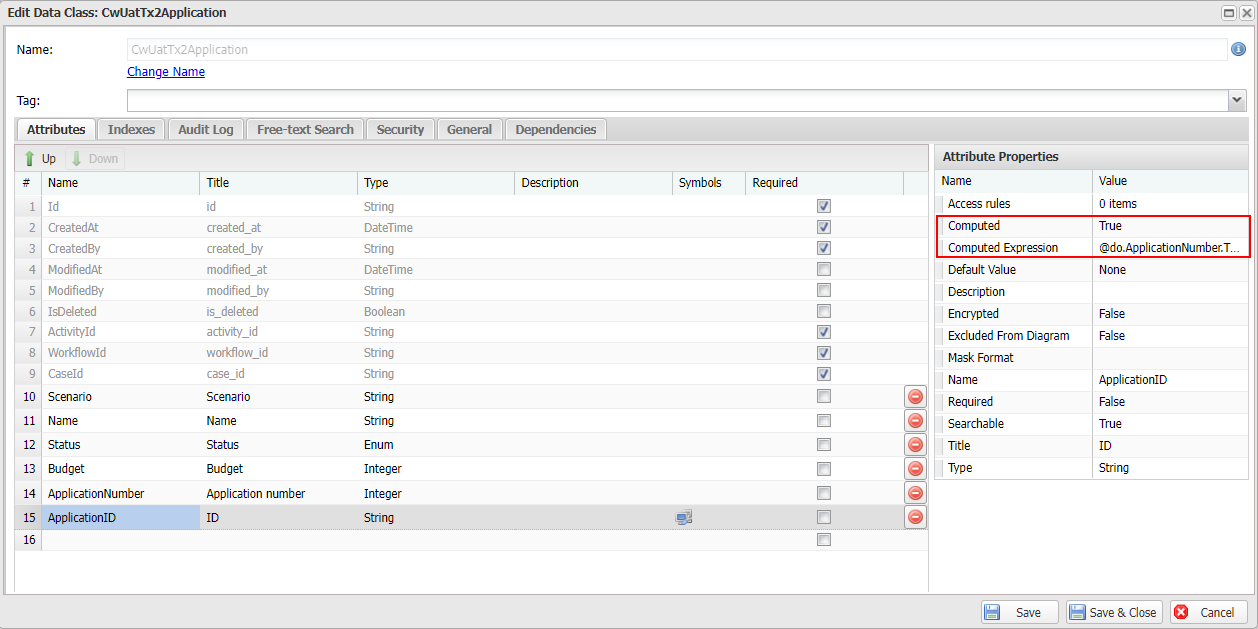
After turning on the Computed setting, you will need to provide a Computed Expression, which Casewhere will use to compute the value. The expression is a simple C# expression, accepting the keyword @do, which is used for accessing the data object attributes. Please note that you can only compute data from other existing data attributes.
Example 1: Compute full name from first name and last name
@do.FirstName + ", " + @do.LastName // "Jone, Doe"
Example 2: Compute a friendly id from an auto-increment value
@do.ApplicationNumber.ToString().PadLeft(5, '0') // "00018", "00019", ...
Auto-increment attribute
Auto-increment is a special computed attribute, which is applied for Integer and Long only. In the data class editor, select an Integer or Long attribute and set Auto Increment to True. When the setting is turned on, Casewhere will assign a new unique number when a new data object is created. The starting value is 1, and it will increment by 1 for each new data object.